 JavaScript
JavaScript
How to optimize react-native map views
React native always has been quite painful when it comes to performance compared to a native application. Today we will focus on increasing the performance and how to optimize react-native map view which has many pegs or markers.
For this example, we use a cluster of markers that change with the region.
First we will check for a library to render react-native map view. https://github.com/react-native-maps/react-native-maps this is the most commonly used map view that used to render most of the maps.
You can install the map view using this link https://github.com/react-native-maps/react-native-maps/blob/master/docs/installation.md It has some tricky parts and if you face any problems when integrating, leave a comment and I will help you out.
In the following link, this full exercise is explained including the installation. Please refer if you need more elaborative.
How to optimize react native map view
Steps involving optimizing
- Add markers to the map in google map view.
- Involve state update in markers and the list when region changes.
- Avoid track view changes after the state is updated.
- Debounce region change calls for time or radius.
With the above steps, you can optimize react-native map view whenever you have a state update on markers or region.
1. Add markers to the map in google map view
If you render the iOS map viwe you can see its performance is better when loading a large number of markers. But when we turn into google maps it is not very optimized and we have to take extra measures to optimize it.
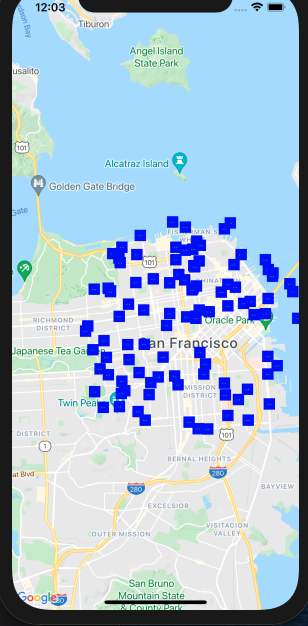
Initial marker view when map is mounted.
The following code will load the markers to the map view. It will load a random number of makers to the app map view.
import React, {useState, useEffect, useCallback} from 'react';
import randomLocation from 'random-location';
import {debounce} from 'lodash';
import {View, StyleSheet, Dimensions} from 'react-native';
import MapView, {Marker, PROVIDER_GOOGLE} from 'react-native-maps';
const INTIAL_REGION = {
latitude: 37.7768006,
longitude: -122.4187928,
};
const LocationView = () => {
const [markers, setMarkers] = useState([]);
const [region, setRegion] = useState(INTIAL_REGION);
const onChangeLocation = useCallback(debounce((region) => {
console.log('debounced region', region);
const locations = new Array(100).fill(undefined).map(() => {
const R = 4000; // meters
const randomPoint = randomLocation.randomCirclePoint(region, R);
return randomPoint;
});
setMarkers(locations);
}, 1000, {trailing: true, leading: false}), []);
useEffect(() => {
onChangeLocation(region);
}, [region]);
// extra code to demonstrate what we will do
const onRegionChange = newRegion => {
setRegion(newRegion);
};
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<MapView
style={styles.map}
provider={PROVIDER_GOOGLE}
onRegionChange={onRegionChange}
initialRegion={{
...INTIAL_REGION,
latitudeDelta: 0.1922,
longitudeDelta: 0.0421,
}}>
{markers.map((point, index) => (
<ImageMarker key={index} point={point} />
))}
</MapView>
</View>
);
};
const ImageMarker = ({point}) => {
const [shouldTrack, setTrack] = useState(false);
const [image, setImage] = useState('https://via.placeholder.com/50/0000FF');
useEffect(() => {
setTrack(true);
setImage('https://via.placeholder.com/50/0000FF');
// Could be a network call to fetch some data or animation which update the state
const timeout = setTimeout(() => {
setImage('https://via.placeholder.com/50');
setTrack(false);
}, 600);
return () => clearInterval(timeout);
}, [point]);
return (
<Marker tracksViewChanges={shouldTrack} coordinate={point} image={{uri: image}} />
);
};2. Involve state update in markers and the list when region changes.
const ImageMarker = ({point}) => {
const [shouldTrack, setTrack] = useState(false);
const [image, setImage] = useState('https://via.placeholder.com/50/0000FF');
useEffect(() => {
setTrack(true);
setImage('https://via.placeholder.com/50/0000FF');
// Could be a network call to fetch some data or animation which update the state
const timeout = setTimeout(() => {
setImage('https://via.placeholder.com/50');
setTrack(false);
}, 600);
return () => clearInterval(timeout);
}, [point]);
return (
<Marker tracksViewChanges={shouldTrack} coordinate={point} image={{uri: image}} />
);
};In the above code, we initially display a marker in blue and make it white after 600 milliseconds to demonstrate a state update.
3. Avoid track view changes after the state is updated
The following will increase the performance by about 50%. The marker should be passed with tracksViewChanges={false} once the state update is over.
For that, we can keep a state variable that needs to be toggled for state updates.
const ImageMarker = ({point}) => {
const [shouldTrack, setTrack] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
setTrack(true);
setImage('https://via.placeholder.com/50/0000FF');
// simulate the network call and the state update
const timeout = setTimeout(() => {
setImage('https://via.placeholder.com/50');
setTrack(false);
}, 600);
return () => clearInterval(timeout);
}, [point]);
// tracksViewChanges should be false when state update is over
return (
<Marker tracksViewChanges={shouldTrack} coordinate={point} image={{uri: image}} />
);
};4. Debounce region change calls for time or radius.
By using Lodash debounce we can avoid constant updates of the UI for the region change.
const onChangeLocation = useCallback(debounce((region) => {
console.log('debounced region', region);
const locations = new Array(100).fill(undefined).map(() => {
const R = 4000; // meters
const randomPoint = randomLocation.randomCirclePoint(region, R);
return randomPoint;
});
setMarkers(locations);
}, 1000, {trailing: true, leading: false}), []);
}, 1000, {trailing: true, leading: false}), []);
Here 1000 means it will wait for 1000 milliseconds before executing the callback function. trailing and leading are the configurations for the debounce function. useCallbackwill make sure it will be initialized once per the component initiation.
If you have any issues with the implementation, please leave a comment to help others as well. Happy Coding!