 OCaml
OCaml
OCaml Data Structures
Ocaml has predefined data structures of tuples, arrays, and lists. There are also mechanisms for defining your own data structures, such as records and variants. In this article, we will discuss about list and tuple.
1. List
List can be define as [ element 1 ; element 2 ; element 3; … ].
Empty List – Empty square brackets [] use to display an empty list.
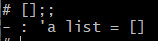
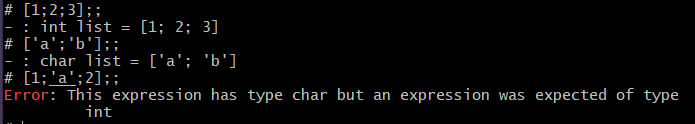
All elements of a list in OCaml must be the same type. Ex – [1;2;3] ;; [‘a’;’b’];; Otherwise there will be an error as “This expression has type … but an expression was expected of type … “. Values in an array should be separate using semicolons.
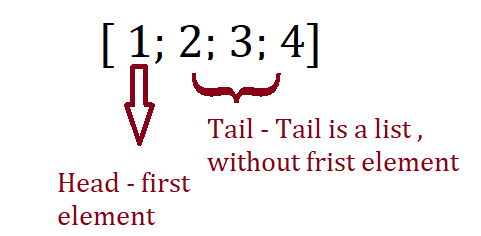
A list has two parts as head and tail. List.hd function gives the head of the list and the List.tl gives the tail of the list.
# let numbers=[1;2;3];; val numbers : int list = [1; 2; 3] # List.hd numbers;; - : int = 1 # List.tl numbers;; - : int list = [2; 3]
So the list can define using cons operator as head :: tail . Therefore [1;2;3] will be equal to the followings;
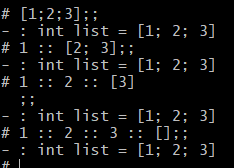
The operator :: is right-associative. So, 1::2::3 means 1::(2::3).
‘a list – List type can be polymorphic. It means that the type of the elements is anything, but all the elements should be the same type.
List.length function can use to get the length of a list.
# List.length;; - : 'a list -> int = <fun> # let numbers=[1;2;3];; val numbers : int list = [1; 2; 3] # List.length numbers;; - : int = 3
Prepend List – You can prepend value to the front of the list as follow;
# let numbers=[1;2;3];; val numbers : int list = [1; 2; 3] # (* prepending a element *) 4::numbers;; - : int list = [4; 1; 2; 3]
Join Lists – Two lists can be joined using the operator @.
# (* join list *) [1;2;3] @ [4;5];; - : int list = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5]
2. Structures – Tuple
Unlike lists, tuples can contain elements of different types. Not like other languages, you can’t name the elements. Therefore you have to remember the order in which they appear.
# type tuple = { a : int ; b : int };;
type tuple = { a : int; b : int; }
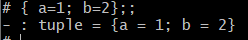
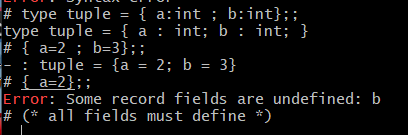
In structure, all fields must be defined.
Related Articles

