AWS
AWS
How to use AWS Ingress ALB with EKS
Overview
Kubernetes has multiple services to facilitate the pod orchestration within the cluster. What we are discussing here is on how to use the AWS Ingress ALB with EKS without using the traditional Load Balancer Service
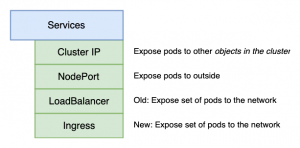
Ingress is very useful than using a normal load balancer. The reason why is on the following diagram
Load Balancer Service
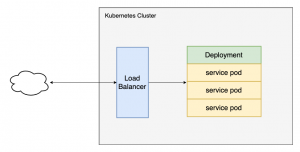
Ingress Service
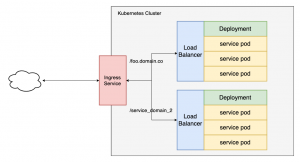
You can use multiple domains as /foo.domain.co or /customter_service to provide the service endpoints within the cluster to the external environment
How to use AWS Ingress ALB with EKS
Ingress has two main parts
- Controller
- Objects
The Controller is a Pod configures to interpret rules. These ingress controllers are provided by both kubernetes and nginx. The most popular one supported by the Kubernetes community. This controller is an Nginx proxy that can run with load balancer rules.
Objects are like a Service Object but it does not do anything on its own. Objects will describe how the layer 7 traffic routes into your cluster, by specifying things like the request path, request domain, and targetKubernetes service, while a service object actually creates service
The AWS ALB with ingress connects with the external environment by using its features.
The repository is here: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller
First of all, why do we need ALB or Ingress? When we have multiple services hosted on the same cluster, it will be a lot easier to work with the controller. Following diagram is a direct reference from the official site regarding how the Ingress with ALB work

[1]: The controller watches for ingress events from the API server. When it finds ingress resources that satisfy its requirements, it begins the creation of AWS resources.
[2]: An ALB (ELBv2) is created in AWS for the new ingress resource. This ALB can be internet-facing or internal. You can also specify the subnets it’s created in using annotations.
[3]: Target Groups are created in AWS for each unique Kubernetes service described in the ingress resource.
[4]: Listeners are created for every port detailed in your ingress resource annotations. When no port is specified, sensible defaults (
80or443) are used. Certificates attaches via annotations.[5]: Rules are created for each path specified in your ingress resource. This ensures traffic to a specific path routes to the correct Kubernetes Service.
Hands on
First, let’s create our Ingress controller and rules for the cluster.
First, apply the RBAC roles for the Ingress Controller.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller/v1.1.2/docs/examples/rbac-role.yaml
Then create the controller for the Ingress.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
name: alb-ingress-controller
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: alb-ingress-controller
spec:
containers:
- name: alb-ingress-controller
args:
# Limit the namespace where this ALB Ingress Controller deployment will
# resolve ingress resources. If left commented, all namespaces are used.
# - --watch-namespace=your-k8s-namespace
# Setting the ingress-class flag below ensures that only ingress resources with the
# annotation kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "alb" are respected by the controller. You may
# choose any class you'd like for this controller to respect.
- --ingress-class=alb
# REQUIRED
# Name of your cluster. Used when naming resources created
# by the ALB Ingress Controller, providing distinction between
# clusters.
- --cluster-name=your-cluster-name
# AWS VPC ID this ingress controller will use to create AWS resources.
# If unspecified, it will be discovered from ec2metadata.
- --aws-vpc-id=created-vpc
# AWS region this ingress controller will operate in.
# If unspecified, it will be discovered from ec2metadata.
# List of regions: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/rande.html#vpc_region
- --aws-region=region
# Enables logging on all outbound requests sent to the AWS API.
# If logging is desired, set to true.
# - ---aws-api-debug
# Maximum number of times to retry the aws calls.
# defaults to 10.
# - --aws-max-retries=10
# env:
# AWS key id for authenticating with the AWS API.
# This is only here for examples. It's recommended you instead use
# a project like kube2iam for granting access.
#- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
# value: KEYVALUE
# AWS key secret for authenticating with the AWS API.
# This is only here for examples. It's recommended you instead use
# a project like kube2iam for granting access.
#- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
# value: SECRETVALUE
# Repository location of the ALB Ingress Controller.
image: docker.io/amazon/aws-alb-ingress-controller:v1.1.2
serviceAccountName: alb-ingress-controller
Save above to ingress-controller.yaml file and apply using the following.
kubectl apply -f ingress-controller.yaml
After that, you can see the controller creates on theKubernetes dashboard of the in kube-system.
![]()
Then you can check the logs on execution here
kubectl logs -n kube-system $(kubectl get po -n kube-system | egrep -o "alb-ingress[a-zA-Z0-9-]+")
After that you can create the ALB for the application. This will provision the ALB in the AWS.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: alb-ingress-service
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/security-groups: sg-00xxxxxx
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/subnets: subnet-xxx, subnet-xxx, subnet-xxxx
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /*
backend:
serviceName: your-lb-service
servicePort: 4001
Check the logs for any possible errors.
kubectl logs -n kube-system $(kubectl get po -n kube-system | egrep -o "alb-ingress[a-zA-Z0-9-]+")
If there is an error for the permissions above all, you should apply the permissions mentioned on this JSON to the role that you are using for the Kubernetes instance
Mostly if there are any subnet issues, it will also reflect on the logs.
Finally, you can log into the AWS console to get the external IP of the ALB you have created. This is visible on the external IP of the Kubernetes Dashboard.
One important thing is URL rewrite is not supporting on AWS ALB Ingress controller. This is the discussion https://github.com/heptio/contour/issues/64
This is what it takes to use AWS Ingress ALB with EKS. Drop a comment for any clarifications.
Happy coding.